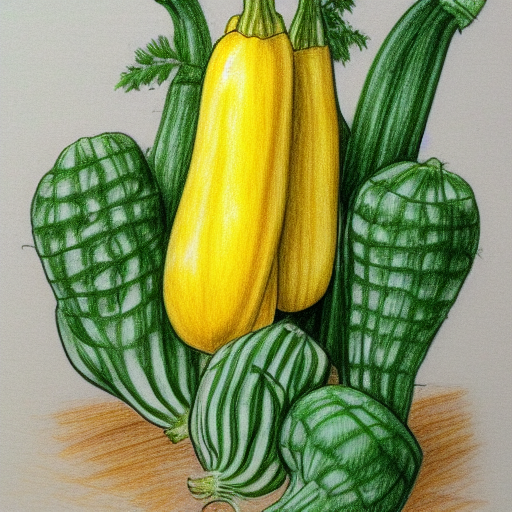
Some yellow squash gardening tips include spacing rows 6 to 12 feet apart, fertilizing with a continuous-release fertilizer, and checking for powdery mildew. Follow these steps to maximize yields and minimize yield loss. Yellow squash needs regular harvesting to be in good shape. If not, they may develop a hard rind or large seeds that affect their flavor and texture.
Space rows of yellow squash 6 to 12 feet apart
Squash are one of the most versatile vegetables, and they are often a good choice for a vegetable garden. They are widely available in the United States and are widely grown in the summer, when temperatures are warm and frost-free. There are many varieties of summer squash, including zucchini and crookneck. You can plant seeds after the danger of frost is past and thin them every 18-24 inches. Harvest them when they are small and the skin is soft.
The spacing between squash plants depends on their type, which includes bush varieties and vines. Bush varieties need to be spaced at four to six feet apart, while vine-type squash need to be spaced six to twelve feet apart. In addition, the plant’s foliage and stems must be at least six inches apart.
Water plants regularly
Water plants regularly when gardening yellow squash. This vegetable prefers moist soil and should receive at least one inch of water per day. The soil should also be enriched with compost and a good source of fertilizer. You can perform a soil test before planting to determine if the soil is rich enough for the type of plant you are growing. In addition, the ground around the plant should be mounded to ensure good drainage.
Squash prefers a slightly acidic soil, but not too acidic. If your soil is too acidic, you should add lime to adjust its pH. It can tolerate a pH as low as 5.5, but you should test the soil first. When watering, avoid watering too much or too little.
Water plants regularly. Ideally, they need one inch of water per week. However, it’s better to water them three times a week. In the first few weeks, you should water them twice a day. As they grow, you should continue watering them until they reach a healthy size.
When watering, try to water when the dew hasn’t dried on the foliage. This way, the water will penetrate deep into the soil. Otherwise, it will evaporate quickly. A good time to water is at the beginning or end of a rain shower. A half-inch rain shower is enough to keep your yellow squash plant healthy.
Fertilize with continuous-release fertilizer
A balanced fertilizer is best for summer squash, as it contains nitrogen for plant growth and potassium and phosphate for fruit production. A balanced fertilizer should be applied every three to four weeks, and the recommended amount is one and a half pounds per 100 square feet of garden area. It is also important to water the area after fertilization so that the nutrients can permeate the soil.
To choose the right fertilizer for squash, make sure to know its growing stage. You should fertilize your zucchini at the early stages of its life cycle, so that it has the energy it needs to produce fruit. Fruiting-crop fertilizers are formulated for this specific type of plant, so you’ll want to choose one labeled for this type of crop. In addition, there are fertilizers for general-use plants, which are generally balanced.
The All-Purpose Vegetable Fertilizer contains a mix of natural ingredients that improves soil aeration and drainage. It also contains proteins and multi-minerals to promote root development. It is non-toxic and has a neutral odor. It also helps plants withstand pests and drought. It is a great choice for established vegetable gardens and container gardening.
If you prefer a liquid fertilizer, mix the fertilizer with water and pour it near the base of the plant. It’s best to apply the liquid fertilizer one to two weeks after granular fertilizer. Avoid fertilization before rainy weather or during a phase when rain is unlikely. You’ll need to water after fertilization to protect the roots.
One of the most popular fertilizers for squash is Miracle-Gro Nature’s Choice. This water-soluble fertilizer is rich in trace minerals that squash needs. It is also organic, meaning that it will help squash grow bigger and better.
Check for powdery mildew
When gardening with yellow squash, you must be on your guard against powdery mildew. This fungus loves high humidity and low light. If you see an infected plant, you should immediately remove it and dispose of it properly. Infected plants should not be composted because this will encourage the spread of the disease.
The first signs of this disease are small, white or gray patches on the leaf surface. You should not wait until the spots start to become larger. This fungus grows by spreading its spores throughout the plant. Once it gets established on the plant, it can spread to the stems and entire leaves. The fungus will then begin to form small root-like structures called mycelia, which are responsible for spreading the disease and causing damage.
You can check for this fungus with sulfur dust or sulfur spray. These products can be found at your local plant nursery or garden center. Another solution is potassium bicarbonate, which can be applied to the plant with water. Potassium bicarbonate is effective against both new and existing powdery mildew, but overuse may cause problems.
Biological fungicides are another good solution for fighting powdery mildew. They are readily available and are environmentally friendly. Chemical fungicides can harm other plants and animals. Therefore, a safe alternative is to use an organic fungicide. You can find them easily online and in most gardening stores.
Powdery mildew is common on vegetable crops and can affect many types of plants. The symptoms of this disease include white spots on the leaves of the vegetable. This disease is not immediately harmful but it can have lasting effects if not treated. Identifying the symptoms will help you prevent it.
Check for cucurbit pests
There are several common pests of yellow squash, which can be found in your garden. These tiny insects feed on the sap of the plant, causing the plant to become weakened. You can easily kill them by dipping the insects into a solution of dish soap and water.
Cucurbit pests can cause major crop damage. They attack the leaves and reduce fruit quality and quantity. They also cause the leaves to curl downwards and sometimes turn brown. Thankfully, there are several effective products to combat these pests. One of the best is Sevin Insect Killer Ready to Spray, which is recommended for early season application before the plants bloom.
Squash bugs are another common pest. These tiny bugs live in the plant’s leaves and eat its sap. This can result in the premature wilting and even death of your cucurbit plants. Squash bugs lay their eggs in clusters of 20 or more.
Squash bugs have a very specific diet. A heavy infestation of squash bugs can kill a plant in a matter of days. If you suspect the presence of squash bugs in your garden, you should take action right away. These insects can spread the cucurbit yellow vine disease bacterium to your plants.
Squash bugs are common summer pests of cucurbits. Fortunately, you can minimize their presence by rotating your crops. If you grow heirloom varieties of squash, you may be more resistant to squash bugs. This is because heirloom varieties have more resistant leaves, making them less vulnerable to pests.
Squash bugs are small insects that feed on the sap of cucurbits. They usually attack pumpkins, summer squash and winter squash, but can also affect other cucurbit crops. To prevent them, you should plant them in an acidic soil that gets ample sunshine.