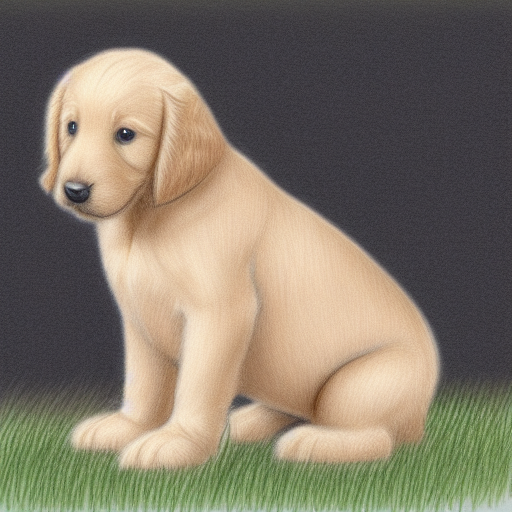
There are various treatment options for golden retriever puppy hip dysplasia. You can treat this problem by using gentle exercise, a healthy diet, and pain relievers. Optimal exercise helps maintain muscle tone and relieve the painful wear and tear on the joints. Swimming is an ideal form of exercise, while prolonged running should be avoided. You can also give your dog a massage to make it feel better.
Treatment options for dog hip dysplasia
Treatment options for golden retriever puppy hip dyslasia vary, depending on the severity of the condition. Some dogs can be helped by simple lifestyle changes while others may require orthopedic surgery. A total hip replacement can result in pain-free walking and a normal gait. The average cost of this surgery is around $1,700, but costs can be as high as $4,500. Your veterinarian can help you choose the best option for your dog.
Hip dysplasia is hereditary and affects approximately 15 percent of canine dogs. Most of the affected dogs are large breeds. This degenerative condition can be delayed or managed, but prevention is always better than cure. The first step in treating golden retriever puppy hip dysplasia is to identify the cause of the condition.
Treatment options for golden retriever puppy hip dysplasia vary based on the severity of the disease and the severity of symptoms. While surgery is not always necessary, pain medication may be prescribed by your veterinarian. Your golden retriever puppy should not jump, run, or participate in strenuous exercises. However, moderate exercise can help strengthen the muscles around the affected joint.
Conservative therapy is one of the most common treatment options for golden retriever puppy hip dyspasia. While conservative therapy does not cure the condition, it can help you manage the symptoms and prevent the condition from progressing. These therapies can include dietary changes, prescription medications, joint supplements, and rehabilitation. If left untreated, the condition can lead to lameness and arthritis. Surgical intervention is typically necessary if conservative treatments are ineffective.
Prevention is also the best treatment for golden retriever puppy hip dysplasie. To prevent the disease, your puppy should be raised on a diet and exercise regimen that promotes healthy joint development. Proper exercise will also help prevent obesity, which can cause diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease.
The first step in treating golden retriever puppy hip dysplasia is to consult with your veterinarian. Your vet will conduct physical tests to assess your dog’s range of motion and any pain or discomfort in the joints. He or she may also use x-rays to determine the severity of the condition. If your puppy has been diagnosed with the disease, don’t panic. The sooner you seek treatment, the sooner it will be possible to make improvements.
Hip dysplasia is a common condition in large breed dogs, which often results in osteoarthritis of the hip joint. It can affect a dog’s quality of life and lead to significant medical expenses. In addition to the pain and discomfort associated with this condition, hip dysplasia can be a significant financial burden to its owner.
A definitive diagnosis of hip dysplasia can be made only after a thorough examination of the dog’s hips. The procedure is usually performed under anesthesia or sedation and is performed by your veterinarian. There are several types of hip x-rays available. A common procedure is the OFA hip x-ray, which is used to diagnose hip dysplasia.
Symptoms of dog hip dysplasia
Dog hip dysplasia is caused by the femur’s failure to properly fit into its socket. It can affect one hip or both, and it is often painful. Symptoms of the condition can appear in puppies as young as four months old, though some dogs may show no symptoms at all until later in life.
The disorder typically affects large breed dogs. Most commonly affected breeds include German shepherds, Saint Bernards, Golden Retrievers, and Labrador retrievers. However, large mixed-breed dogs are also at risk. It is important to educate yourself about the proper diet for large-breed dogs and exercise to reduce the risk of the disease.
A moderate exercise routine is essential for dogs with hip dysplasia. Regular runs and walks can strengthen the gluteal muscles and help your dog stay active. But avoid excessive exercise, as it places unnecessary pressure on the joints. Avoid playing Frisbee or jumping, as these activities can cause damage to the joints.
Dogs with hip dysplasia are prone to pain, limping, and reduced mobility. Treatment may involve medication or surgery. A veterinarian can provide you with a clear understanding of the condition and how it affects your dog. If treatment fails, it can lead to osteoarthritis in the affected joints.
Dog hip dysplasia is believed to be a hereditary condition. However, environmental factors, such as obesity, may play a role as well. The onset of the disease may occur early or in the late stages of a dog’s life. Breeding dogs with weaker skeletal stock is also a risk factor.
Dogs suffering from hip dysplasia should be examined regularly by a vet. Early detection is important to avoid further complications and expensive surgeries. Prevention is better than cure, and early visits to the vet will ensure your dog’s health for the rest of its life. The vet can provide treatment for the condition, including hot and cold treatment and cold laser therapy.
Treatment for dog hip dysplasia is similar to that used in humans. Depending on the severity of the disease, the dog may require a total hip replacement (THR). A total hip replacement involves inserting plastic and metal implants in the affected hip. This procedure restores hip function and eliminates pain associated with the disorder.
Treatment options for dog elbow dysplasia
Treatment options for dog elbow dysplasia vary depending on the cause and severity of the problem. In mild to moderate cases, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and joint supplements may alleviate the pain and inflammation. Other options may include integrative therapies, which work to improve the mobility and flexibility of joints and decrease inflammation and pain.
If the dog suffers from mild to moderate elbow dysplasia, arthroscopic surgery may be an option. This minimally-invasive procedure can take between 15 and 30 minutes per elbow and is considered safe for most dogs. The recovery period is relatively short and most dogs can return to normal activity within a few weeks.
Treatment for dog elbow dysplasia depends on the severity of the condition and the age of the animal. However, most dogs respond well to pain-relieving therapies and surgery. These treatments can help them lead happy and healthy lives. However, the pain, swelling, and debilitating symptoms of the condition can shorten a dog’s life.
Surgery for elbow dysplasia involves fragment removal, incongruence surgery, or salvage surgery. The goal of fragment removal surgery is to remove loose fragments of the elbow joint. The surgery can be performed arthroscopically or with a direct surgical approach. Although these options have proven effective in some cases, some dogs may experience lameness even after surgery. They may also experience secondary osteoarthritis in their elbows.
The most common symptom of dog elbow dysplasia is lameness. Dogs with this condition typically limp after exercise and do not recover until they rest. Dogs with the disease may also be reluctant to go for long walks and play. Symptoms of dog elbow dysplasia may also include limited range of motion and pain while extending or flexion. Furthermore, dogs with the disease may experience pain when laying in the sternal position.
Dogs with elbow dysplasia are often lame and may develop osteoarthritis as they get older. The condition is often inherited and causes the elbow joint to develop abnormally. The elbow joint is formed of three bones. When the elbow develops, deterioration of the cartilage causes inflammation, which results in lameness and arthritis in the affected limb.
Treatment options for dog elbow dysplasia depend on the severity of the disease entities that accompany it. Some cases may require specialist veterinary orthopaedic treatment. Osteochondritis can cause damage to the joint surface and can result in severe overload.